The Role of Electric Mobility in Social Transformation and Its Contribution to Sustainable Development
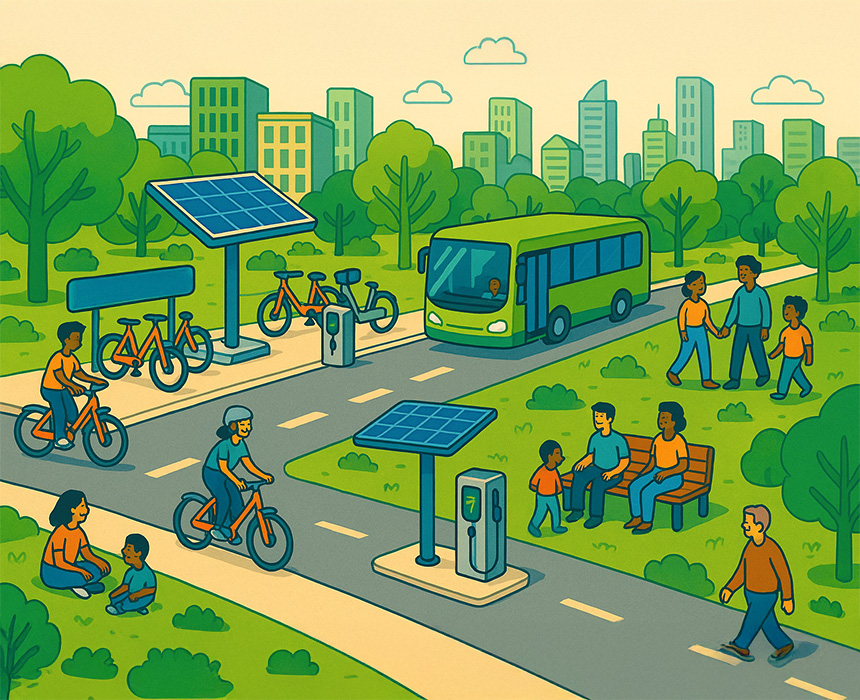
Electric mobility is becoming a driving force of profound transformation not only in the transport sector but also across every aspect of social life. It spans a wide range of impacts — from energy consumption and urban planning to air quality and job creation. This transformation creates an ecosystem that simultaneously nourishes the environmental, economic and social dimensions of sustainable development.
1. Environmental Dimension: Transition to Clean Energy and Carbon Footprint Reduction
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles reduces dependence on fossil fuels and lowers greenhouse gas emissions. Improvements in urban air quality, reductions in noise pollution and integration of renewable energy sources into charging infrastructure are the cornerstones of environmental sustainability. This is critical both for individual health and for maintaining ecosystem balance.
2. Economic Dimension: New Business Models and Job Opportunities
Electric mobility creates new employment opportunities across a wide array of sectors — from battery manufacturing and charging station deployment to software development and energy management. The start-up ecosystem, innovative business models and public-private partnerships accelerate this transformation. Increased domestic production capacity and export potential strengthen the economy.
3. Urban Planning and Smart Infrastructure
Smart cities are leveraging the data and digital services offered by electric mobility to build more flexible, accessible and sustainable transport networks. Strategic placement of charging stations, integration with micro-mobility solutions and real-time traffic management bring a new vision to urban planning.
4. Social Access and Equity
Electric vehicle sharing platforms, micro-mobility services and publicly supported charging infrastructure make transport more accessible and fair. Providing disadvantaged groups with access to clean transport solutions enhances social equity and quality of life.
5. Integration of Energy and Transport Sectors
Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) and vehicle-to-home (V2H) technologies allow users to operate their electric vehicles not only as consumers but also as energy suppliers. This increases grid flexibility and offers users new income opportunities.
6. Innovation and Technological Development
Electric mobility has become a stage for numerous technological innovations — from battery chemistries to AI-powered route planning. The adoption of open standards and protocols stimulates innovation and strengthens the interoperability of the ecosystem.
7. Education and Awareness
Awareness campaigns, training programs and incentives are critical to help society adapt to electric mobility. Incorporating clean energy and sustainable transport topics into school and university curricula prepares future generations for this transition.
8. Regulatory Frameworks and Incentive Mechanisms
Tax reductions, grant programs and infrastructure support for electric mobility are increasing in line with sustainable development goals. Transparent data management, consumer rights and compliance with standards ensure the effectiveness of these incentives.
9. Cultural Transformation and Behavioural Change
Electric vehicle ownership and sharing are reshaping individual travel habits. A clean, quiet and digitally supported transport culture is emerging. Combined with increased environmental awareness and strengthened social responsibility, this culture supports sustainable lifestyles.
10. Looking Ahead: Integrated Mobility Ecosystems
In the near future, electric mobility will evolve into a multi-layered ecosystem integrating autonomous vehicles, renewable energy systems, micro-mobility solutions and digital payment platforms. This ecosystem will make it easier for cities to achieve carbon-neutral targets while accelerating economic and social development.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Electric mobility is becoming a powerful engine of social transformation and sustainable development. The combination of environmental benefits, economic opportunities, social access and technological innovation will make future cities more liveable, fair and resilient. An electric mobility ecosystem supported by joint efforts from government, private sector and society will play a key role in achieving sustainable development goals.